Foundations of AI
Overview
This lesson establishes the core conceptual framework for artificial intelligence. It covers:
AI definitions (1950s → present): From symbolic “machines that think” (Turing, McCarthy) to data-driven systems that learn, generalize, and act under uncertainty
AI history: Early symbolic AI → expert systems → AI winters → statistical machine learning → deep learning → foundation & generative models
Field hierarchy: Artificial Intelligence ⊃ Machine Learning ⊃ Deep Learning (overlapping with statistics, optimization, neuroscience)
Machine learning paradigms:
- Supervised: classification, regression
- Unsupervised: clustering, dimensionality reduction, density estimation
- Semi-supervised: combined labeled + unlabeled data
- Reinforcement learning: policy learning via reward signals
- Supervised: classification, regression
AI subfields: NLP, computer vision, robotics, planning, reasoning, speech, multi-agent systems, recommender systems, AI safety
Symbolic vs modern AI: Rules vs learned representations; human-engineered vs data-driven knowledge; interpretable vs opaque; brittle vs scalable; low compute vs high compute
State of AI (2025–26): Strong pattern recognition and generation; weak causal reasoning, grounding, autonomy, and reliability—capabilities often overstated outside research
These topics provide the necessary background, shared vocabulary, and critical perspective for all subsequent technical material in the course.
Learning Objectives
After completing this lesson, students will be able to:
AI definitions: Distinguish weak vs strong AI; narrow AI vs AGI vs superintelligence
AI history: Dartmouth (1956) → symbolic AI → expert systems → AI winters → deep learning → foundation models (2025–26)
Concept hierarchy: Deep Learning ⊂ Machine Learning ⊂ Artificial Intelligence; symbolic, evolutionary, Bayesian methods alongside ML
Learning paradigms:
- Supervised: labeled data (e.g., spam detection)
- Unsupervised: structure discovery (e.g., clustering)
- Semi-supervised: limited labels + large unlabeled data
- Reinforcement learning: reward-driven decision making
AI subfields: Computer vision, NLP, robotics, knowledge representation, planning, generative AI
Symbolic vs data-driven AI: Hand-coded rules vs learned models; interpretable vs opaque; brittle vs scalable; logic-based vs statistical development
AI pipeline: Problem definition → data collection → preprocessing → modeling → training → evaluation → deployment → monitoring
Current capabilities vs gaps: Strong large-scale pattern recognition; weak understanding, causality, long-horizon planning
AI hype & limits: Media overgeneralization, benchmark gaming, anthropomorphic language; open questions in reasoning, alignment, and autonomy ## What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is the branch of computer science that studies and develops systems capable of performing tasks that would require intelligence if carried out by humans.
Core definitions
Weak (narrow) AI
Systems designed for specific tasks that appear intelligent in a limited domain.
Examples: speech recognition, image classification, chess-playing programs, recommendation algorithms.
All current operational AI systems (2026) fall into this category.Strong (general) AI
Systems that possess the same intellectual abilities as a human across a wide range of cognitive tasks.
Also called artificial general intelligence (AGI).
No such system exists as of 2026.Superintelligence
An intellect that substantially exceeds the cognitive performance of humans in virtually all domains of interest.
Hypothetical; remains a topic of theoretical discussion and long-term speculation.
Historical and practical definitions
Early definitions (1950s–1960s)
Machines that could simulate any aspect of human intelligence, including learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding.
Mid-period definitions (1970s–1990s)
Systems capable of goal-directed adaptive behavior or of performing tasks that involve high-level mental processes such as reasoning or decision-making.
Contemporary practical definitions (2000s–2026)
Computational systems that exhibit intelligent behavior by perceiving their environment, taking actions that maximize the chance of achieving specified goals, or by learning from data to improve performance on a task.
Russell and Norvig (2020, updated editions) provide four main perspectives that have shaped the field:
- Thinking humanly → cognitive modeling (imitating human thought processes)
- Thinking rationally → logical reasoning (laws of thought approach)
- Acting humanly → behavioral evaluation (Turing Test style)
- Acting rationally → rational agent design (maximizing expected utility)
Most modern research follows the rational agent view: an intelligent agent is one that acts to achieve the best expected outcome given available information.
AI seasons: periods of progress and setbacks
The history of AI is characterized by alternating seasons of enthusiasm (summers) and disappointment (winters).
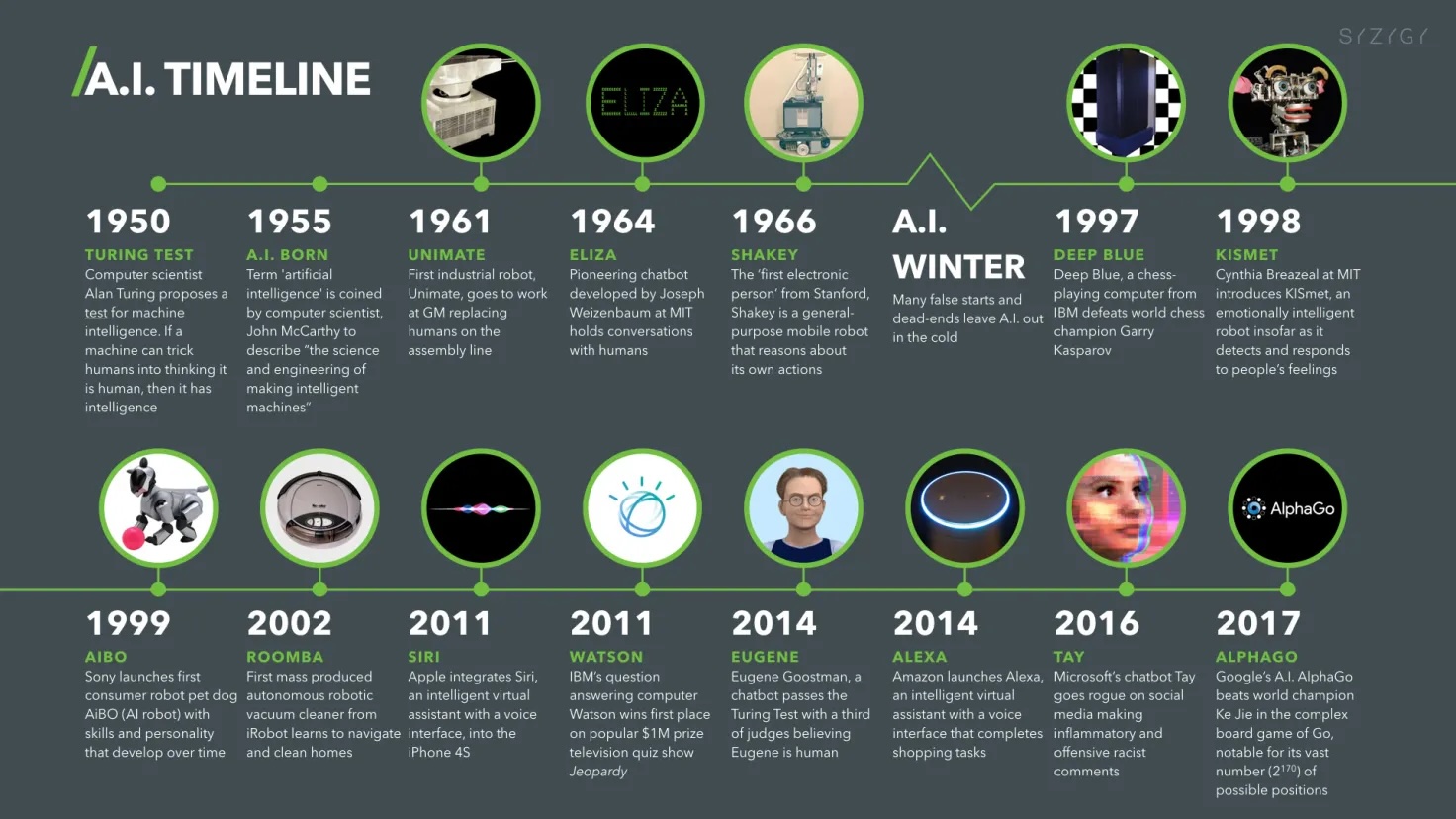
Figure 1 presents a chronological overview of major events starting from early programs such as ELIZA.
First AI summer (1956–1973)
Intense optimism following the Dartmouth Conference. Significant early achievements in symbolic reasoning and problem-solving.First AI winter (1974–1980)
Reduced funding and interest after failure to achieve broad promises. Limited hardware, data, and algorithmic power led to stagnation.
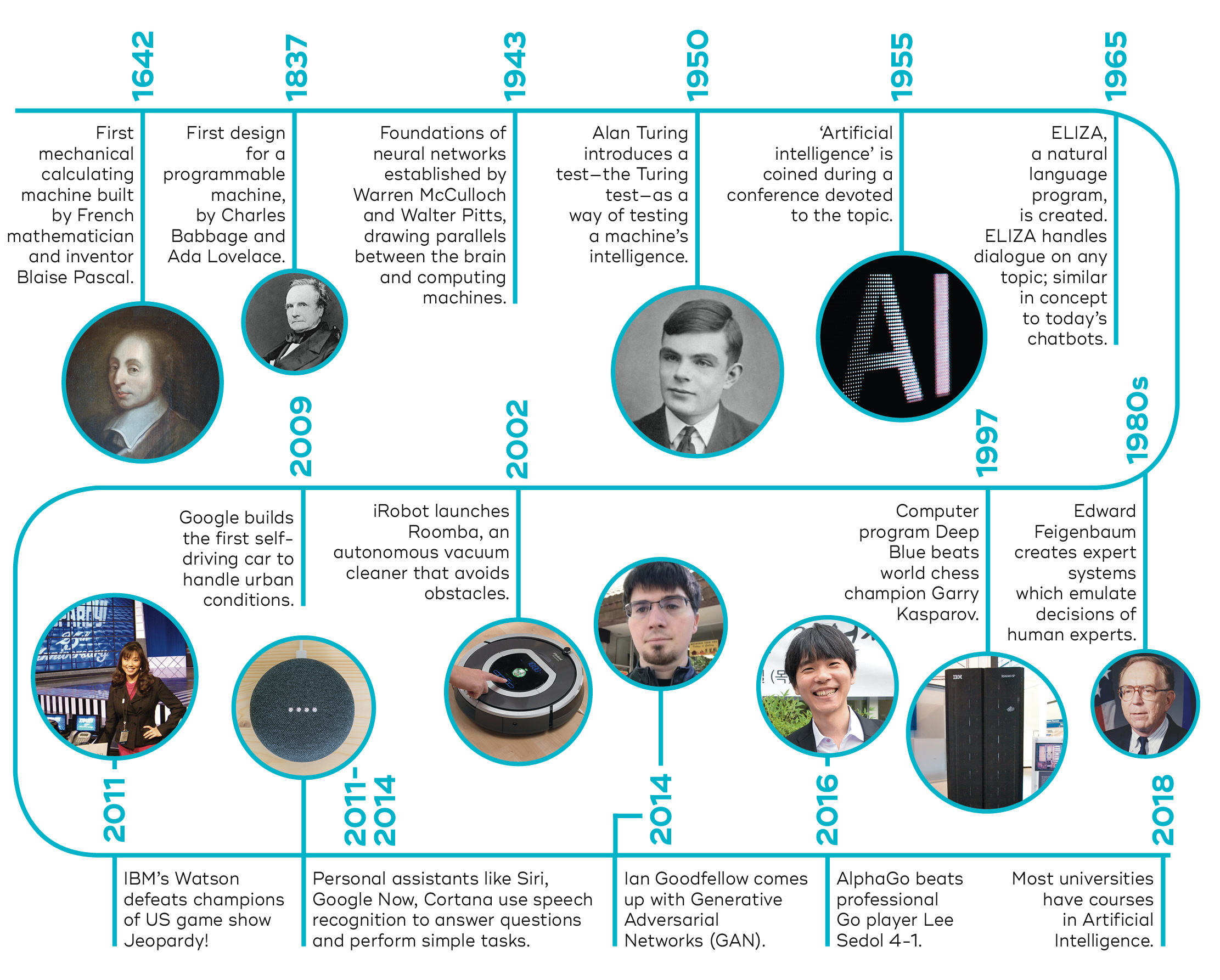
Figure 2 offers a visual summary of key milestones across the decades, highlighting shifts in approaches.
Second AI summer (1980–1987)
Revival through expert systems and commercial applications. Large-scale rule-based systems deployed in industry and medicine.Second AI winter (1987–1993)
Collapse of the expert systems market due to high maintenance costs, brittleness, and inability to handle uncertainty. Funding and research activity declined sharply.AI spring / recovery (1993–2011)
Gradual shift to statistical methods, machine learning, and practical applications. Key events include Deep Blue (1997), increased use of support vector machines, and Watson (2011).
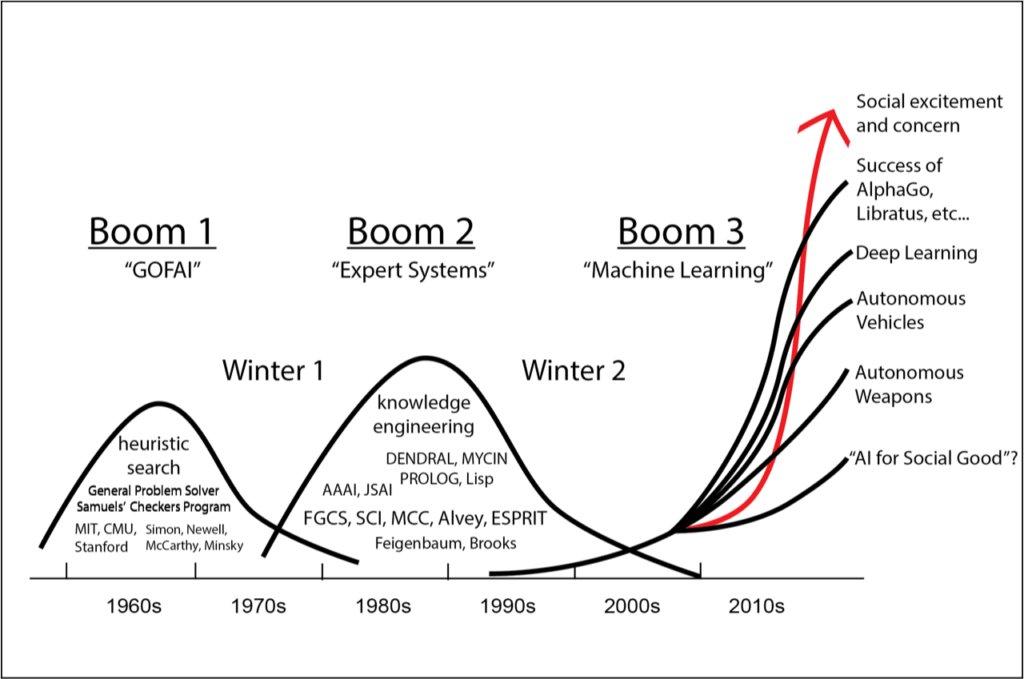
Figure 3 depicts the recurring wave pattern of progress, hype, disillusionment, and recovery.
- Third AI summer / deep learning boom (2012–present)
Explosive growth driven by deep neural networks, large datasets, GPU acceleration, and massive compute resources. Breakthroughs in vision (2012), games (2016), and language (2018–2026). Sustained investment and rapid progress continue into 2026 with foundation models and multimodal systems.
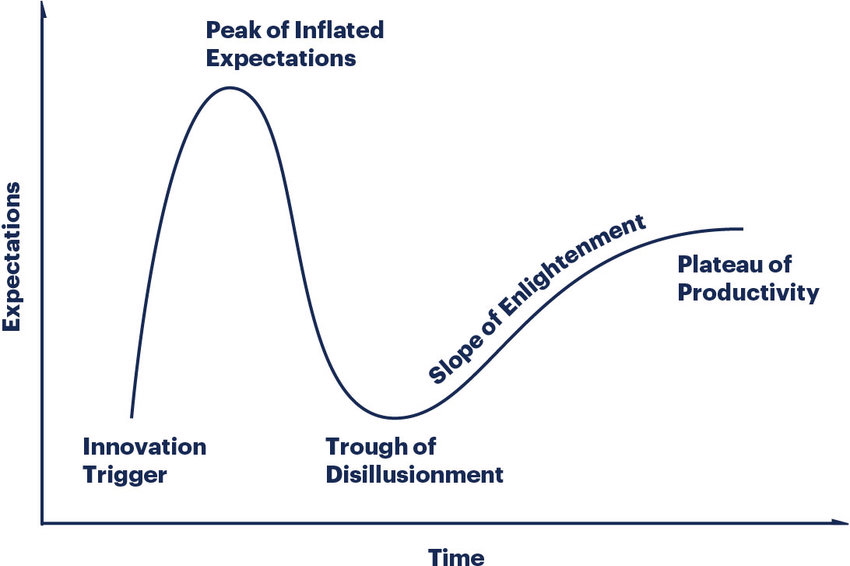
Figure 4 shows a formalized view of technology maturity stages, with troughs corresponding to AI winters and current plateau of productivity for deep learning applications.
These cycles reflect recurring patterns: over-optimism, technological limitations, funding cuts, then gradual recovery through new paradigms and improved infrastructure.
Overview of subfields of AI in plain language
The field of artificial intelligence consists of several interconnected subfields. The following hierarchy provides a structured overview of major branches and their primary areas of focus.
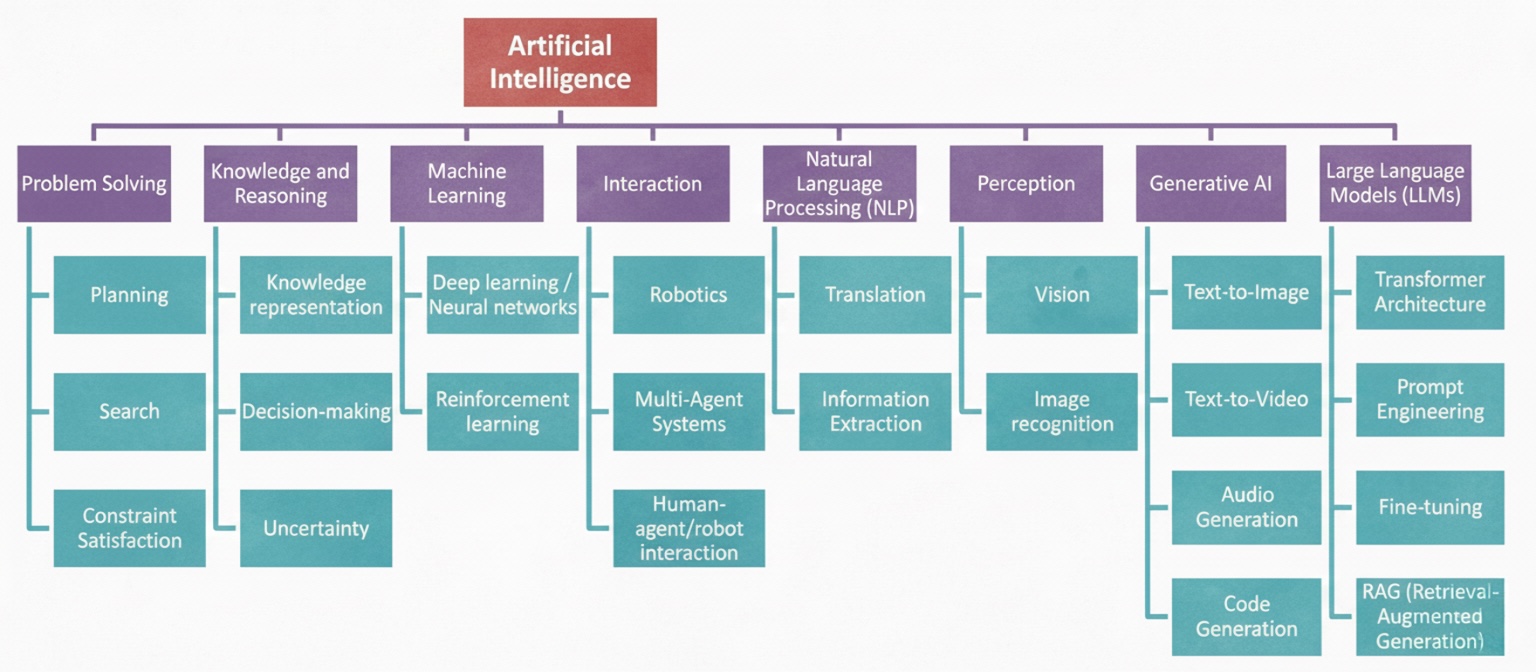
Figure 5 presents a comprehensive map of AI subfields organized under the central node of Artificial Intelligence. The main branches are Problem Solving, Knowledge and Reasoning, Machine Learning, Interaction, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Perception, Generative AI, and Large Language Models (LLMs). Each branch contains representative sub-areas.
Problem Solving
Focuses on finding solutions to complex problems through algorithmic methods.
- Planning: generating sequences of actions to reach goals
- Search: exploring possible states to find optimal paths
- Constraint Satisfaction: solving problems under restrictions (e.g., scheduling, configuration)
Knowledge and Reasoning
Deals with representing, storing, and manipulating knowledge to draw inferences.
- Knowledge representation: formal structures for facts and relations
- Decision-making: choosing actions based on goals and beliefs
- Uncertainty: handling incomplete or probabilistic information
Machine Learning
Enables systems to improve performance from data without explicit programming.
- Deep learning / Neural networks: layered models for pattern recognition
- Reinforcement learning: learning through trial-and-error with rewards
Interaction
Concerns systems that act in physical or social environments.
- Robotics: embodied AI for manipulation and navigation
- Multi-Agent Systems: coordination among multiple intelligent entities
- Human-agent/robot interaction: natural communication and collaboration
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Processes and generates human language.
- Translation: converting text between languages
- Information Extraction: identifying structured data from text
Perception
Interprets sensory input from the environment.
- Vision: understanding images and video
- Image recognition: classifying or detecting objects in visual data
Generative AI
Creates new content resembling training data.
- Text-to-Image: generating images from text descriptions
- Text-to-Video: producing video sequences from prompts
- Audio Generation: synthesizing speech or music
- Code Generation: writing program code from natural language
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Foundation models specialized in language tasks at a massive scale.
- Transformer Architecture: core mechanism enabling parallel processing
- Prompt Engineering: designing inputs to guide model behavior
- Fine-tuning: adapting pretrained models to specific tasks
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): combining retrieval of external knowledge with generation
These subfields overlap significantly in modern AI systems. For example, large language models often integrate elements of NLP, generative AI, and reasoning; perception and interaction are combined in robotics applications; and machine learning underpins nearly all current practical advances across branches.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence focused on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data, without being explicitly programmed for the task.
Formal definition (Mitchell 1997): A computer program is said to learn from experience \(E\) with respect to some class of tasks \(T\) and performance measure \(P\), if its performance at tasks in \(T\), as measured by \(P\), improves with experience \(E\).
Key characteristics: - Data-driven: relies on patterns in training data rather than hardcoded rules - Generalization: ability to perform well on unseen data - Adaptability: improves with more data or retraining - Types: supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, reinforcement
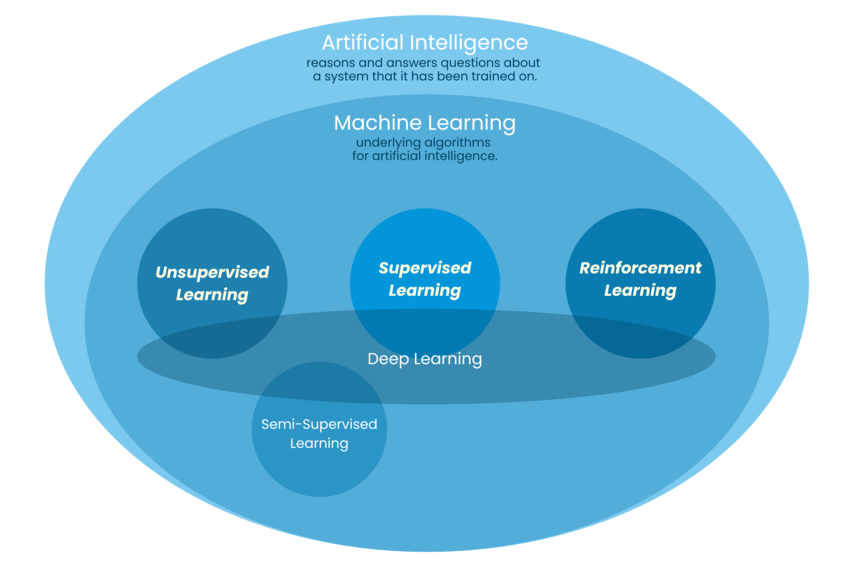
Relationship within AI: - AI encompasses all approaches to intelligent systems - Machine learning is the dominant paradigm in modern AI - Deep learning is a specialized subset of machine learning using multi-layer neural networks
Differences between rule-based and machine learning approaches: spam email detection example
Consider the problem of classifying emails as spam or not spam.
Rule-based approach (symbolic AI)
Knowledge is explicitly programmed as if-then rules by human experts.
Example rules:
- IF email contains “free money” THEN spam
- IF sender not in contacts AND has attachments THEN spam
- IF too many uppercase words THEN spam
Advantages: interpretable, no training data required, fast inference.
Disadvantages: brittle to variations, requires constant manual updates, poor scalability.
Machine learning approach
Model learns patterns automatically from labeled examples (spam/non-spam emails).
Process:
1. Feature extraction: convert email to numerical features (word counts, sender info, links, etc.)
2. Training: use algorithms like Naive Bayes, SVM, or neural networks on labeled dataset
3. Prediction: classify new emails based on learned probabilities or decision boundaries
Advantages: adapts to new patterns, handles nuanced features, improves with data.
Disadvantages: requires large labeled dataset, lower interpretability.
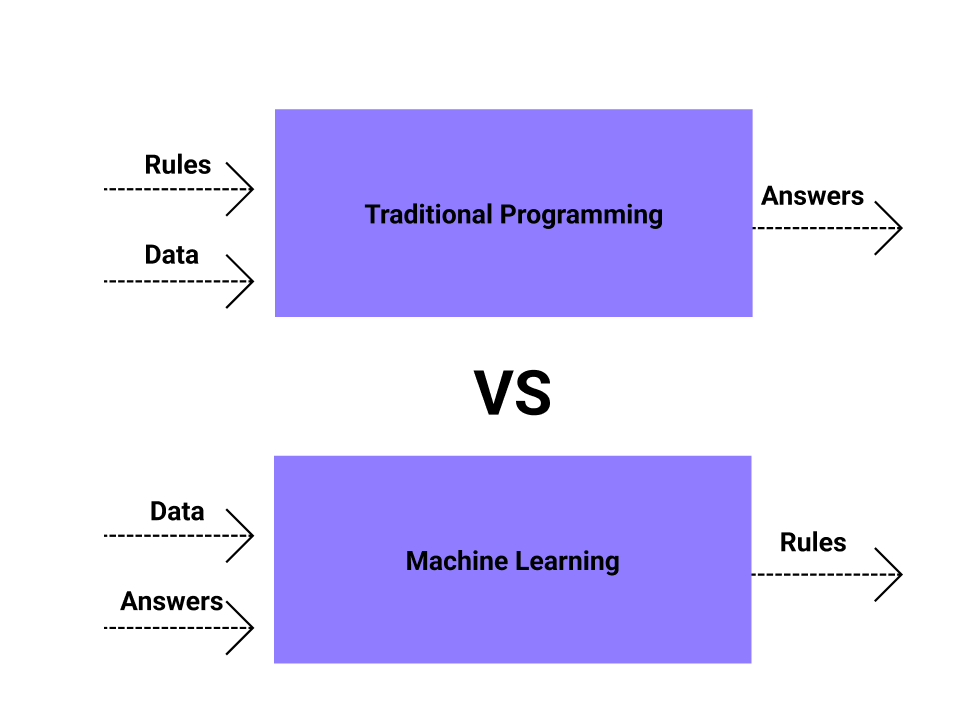
Figure 6 illustrates the fundamental difference in structure: rule-based systems apply explicit, hand-crafted logic trees, while machine learning systems derive decision rules from labeled training data through optimization.
Comparison table:
| Aspect | Rule-based | Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge source | Human experts | Labeled data |
| Adaptability | Manual updates | Retraining with new data |
| Handling variations | Poor (rule evasion easy) | Good (learns patterns) |
| Interpretability | High | Low to medium |
| Initial setup | Rule engineering | Data collection and labeling |
| Maintenance | Frequent rule adjustments | Periodic model retraining |
Subcategories of machine learning
Machine learning is commonly divided into four primary paradigms based on the nature of the available data, the type of supervision provided during training, and the learning objective. These are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. A fifth category, self-supervised learning, has gained prominence in recent years, particularly for pretraining large models.
Supervised learning
In supervised learning, the algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset where each input example is paired with the correct output (label or target value). The model learns to approximate the mapping from inputs to outputs and is evaluated on its ability to generalize to new, unseen examples.
Main task types: - Classification: predict discrete class labels (e.g., email is spam or not spam, image shows cat or dog) - Regression: predict continuous values (e.g., house price, temperature, stock return)
Typical evaluation metrics: - Classification: accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, ROC-AUC - Regression: mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE), R² coefficient
Figure 7 shows supervised learning as one of the core branches within machine learning, nested inside the broader artificial intelligence field.
Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning operates on data without any output labels. The goal is to discover hidden structure, patterns, or relationships in the data itself.
Main task types: - Clustering: grouping similar examples (e.g., customer segmentation, topic discovery in documents) - Dimensionality reduction: finding compact representations of high-dimensional data (e.g., PCA, t-SNE, UMAP for visualization or preprocessing) - Density estimation and generative modeling: modeling the probability distribution of the data (e.g., anomaly detection, data synthesis)
Semi-supervised learning
Semi-supervised learning combines a small amount of labeled data with a large amount of unlabeled data. It is particularly valuable when obtaining labels is expensive or time-consuming (common in medical imaging, speech recognition, and web-scale text).
Common techniques: - Self-training / pseudo-labeling: use model predictions on unlabeled data as pseudo-labels for retraining - Consistency regularization: encourage invariant predictions under different augmentations of the same input - Graph-based methods: propagate labels through a similarity graph of all data points
Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning focuses on sequential decision-making in an interactive setting. An agent learns by trial and error through interaction with an environment, receiving scalar rewards (or penalties) for its actions.
Core elements: - Agent - Environment - State - Action - Reward signal - Policy (strategy for choosing actions)
Main families: - Value-based methods (e.g., Q-learning, Deep Q-Networks) - Policy-based methods (e.g., REINFORCE, PPO) - Actor-critic methods
Typical applications: game playing, robotics control, recommendation systems with long-term optimization.
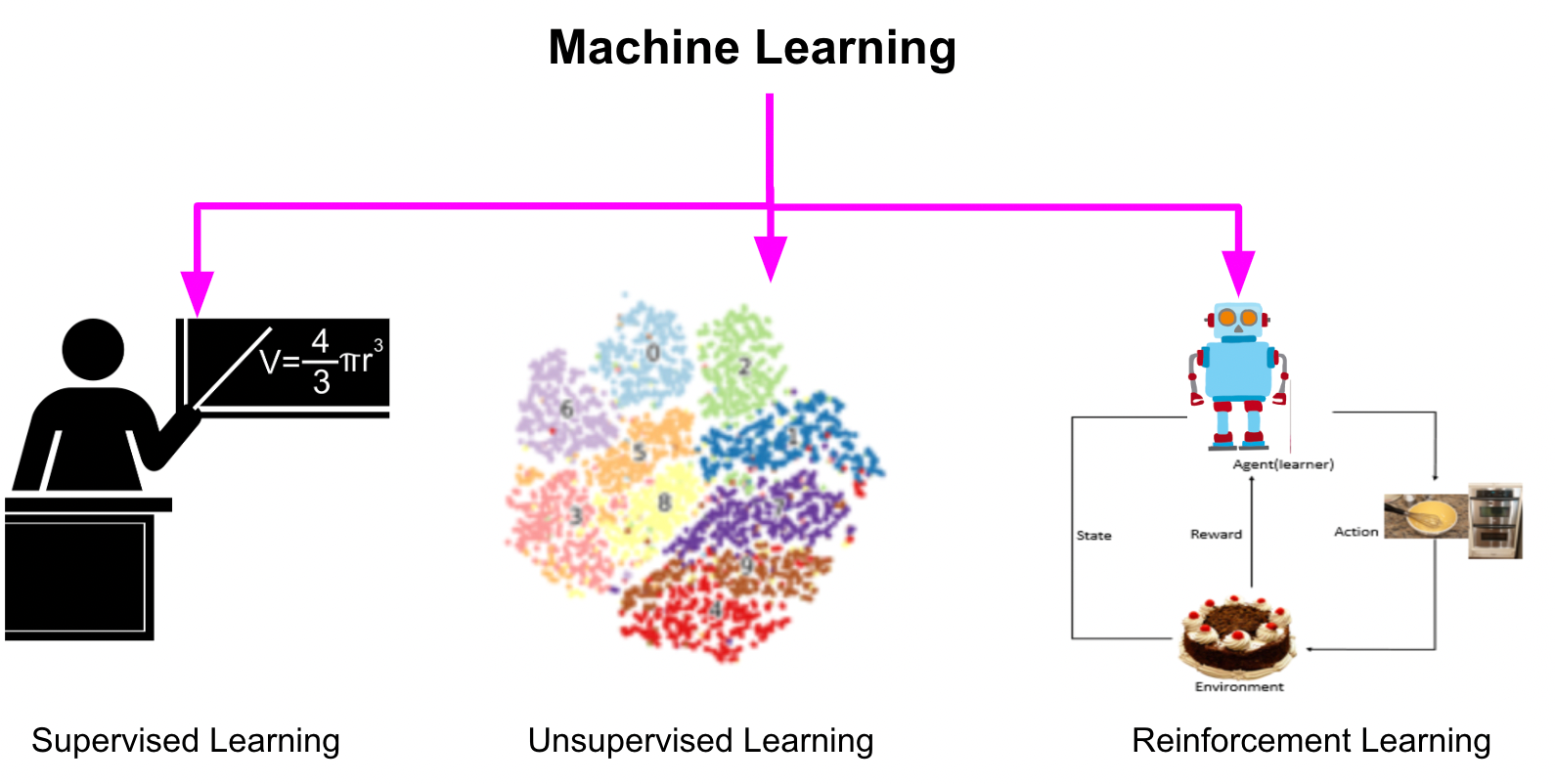
Figure 8 provides a visual summary of the core machine learning paradigms, highlighting input types, feedback mechanisms, and typical applications for supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Semi-supervised learning is often positioned as a hybrid between supervised and unsupervised.
Hype compared to reality in current AI systems
Large-scale AI systems in 2025–2026, primarily foundation models with hundreds of billions to trillions of parameters, exhibit impressive performance across many benchmarks but remain subject to well-documented technical limitations. The following evaluation contrasts empirically measured capabilities with common claims encountered in academic papers, company announcements, media reporting, and public discussion.
Common claims vs documented capabilities
Claim: Current AI understands language like humans do
Reality: Systems perform statistical pattern matching and next-token prediction at scale. They exhibit surface-level fluency and correlation capture but lack genuine semantic understanding, intentionality, or world models in the human sense. Failure modes include hallucinations, reversal curse, and inability to reliably track long-term factual consistency without external retrieval.Claim: AI has achieved or is very close to general intelligence
Reality: All operational systems remain narrow. They excel in specific domains (language modeling, code generation, image synthesis) when trained on vast data but fail catastrophically outside distribution or on novel reasoning tasks requiring systematic generalization. No system demonstrates broad, flexible intelligence across unrelated domains without task-specific fine-tuning or prompting.Claim: Scaling laws ensure that further increases in compute, data, and parameters will solve remaining problems
Reality: Scaling continues to yield diminishing but positive returns on many benchmarks. However, plateaus and saturation have been observed on several standardized tests (MMLU, BIG-Bench Hard, GPQA). Emergent capabilities have slowed in visibility; architectural and algorithmic innovation remain necessary for breakthroughs beyond current trends.Claim: Models reason step-by-step like humans
Reality: Chain-of-thought prompting and its variants improve performance on reasoning benchmarks. However, the underlying computation is parallel token prediction, not sequential symbolic reasoning. Models frequently produce post-hoc rationalizations rather than genuine deductive chains. Errors in early steps propagate irrecoverably.Claim: AI systems are already superhuman across most cognitive tasks
Reality: Superhuman performance exists in narrow, well-defined domains (chess, Go, protein folding, some image classification tasks, certain multiple-choice benchmarks). On open-ended, real-world tasks involving planning, causal reasoning, physical intuition, or long-horizon coordination, even the largest models lag far behind skilled humans.Claim: Current models are conscious / sentient / self-aware
Reality: No empirical evidence supports consciousness or subjective experience. Behavior that appears self-referential or introspective arises from training on human text describing such concepts. All internal states are differentiable computations without qualia or unified agency.Claim: AI will replace most knowledge workers in the near term
Reality: AI augments productivity in writing, coding, analysis, and content generation. Full autonomous replacement remains limited to highly structured, repetitive, or low-stakes tasks. Reliability, accountability, and edge-case handling require human oversight in professional settings.
Key fundamental limitations (2025–2026)
- Distribution shift and out-of-distribution generalization remain unsolved
- Lack of causal understanding and robust counterfactual reasoning
- Poor long-context fidelity and reliable memory over very extended sequences
- Vulnerability to adversarial examples, prompt injection, and jailbreaking
- High inference cost and energy consumption for frontier models
- Inability to perform true open-ended planning or self-directed learning without human-defined objectives
- Absence of intrinsic motivation, curiosity, or autonomous goal formation
Summary table of select capabilities vs limitations
| Domain / Task Type | Observed Capability Level (2025–2026) | Typical Claim Level | Key Remaining Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple-choice academic benchmarks | Superhuman on many | Human-level or better | Saturation on hardest subsets |
| Open-ended question answering | High fluency, frequent factual errors | Reliable expert knowledge | Hallucination, retrieval dependence |
| Code generation | Useful for many routine tasks | Expert programmer replacement | Logical errors in complex systems |
| Multimodal reasoning | Strong on aligned tasks | Human-like visual-language understanding | Causal and physical commonsense |
| Long-horizon planning | Poor without scaffolding | Strategic reasoning like humans | No reliable multi-step execution |
| Real-world agency / autonomy | Extremely limited | Independent agent deployment | No robust long-term goal pursuit |
These observations are drawn from independent evaluations (e.g., LMSYS Chatbot Arena, HELM, Model Cards, academic stress tests), not solely from self-reported company leaderboards.